Running a large language model (LLM) on your computer is now easier than ever.
You no longer need a cloud subscription or a massive server. With just your PC, you can run models like Llama, Mistral, or Phi, privately and offline.
This guide will show you how to set up an open-source LLM locally, explain the tools involved, and walk you through both the UI and command-line installation methods.
Understanding Open Source LLMs
An open-source large language model is a type of AI that can understand and generate text, much like ChatGPT. But it can function without depending on external servers.
You can download the model files, run them on your machine, and even fine-tune them for your use cases.
Projects like Llama 3, Mistral, Gemma, and Phi have made it possible to run models that fit well on consumer hardware. You can choose between smaller models that run on CPUs or larger ones that benefit from GPUs.
Running these models locally gives you privacy, control, and flexibility. It also helps developers integrate AI features into their applications without relying on cloud APIs.
Choosing a Platform to Run LLMs Locally
To run an open source model, you need a platform that can load it, manage its parameters, and provide an interface to interact with it.
Three popular choices for local setup are:
We’ll use Ollama as the example in this guide since it’s widely supported and integrates easily with other tools.
Installing Ollama
Ollama provides a one-click installer that sets up everything you need to run local models.
Visit the official Ollama website and download the Windows installer.

Once downloaded, double-click the file to start installation. The setup wizard will guide you through the process, which only takes a few minutes.
When the installation finishes, Ollama will run in the background as a local service. You can access it either through its graphical desktop interface or using the command line.
After installing Ollama, you can open the application from the Start Menu. The UI makes it easy for beginners to start interacting with local models.
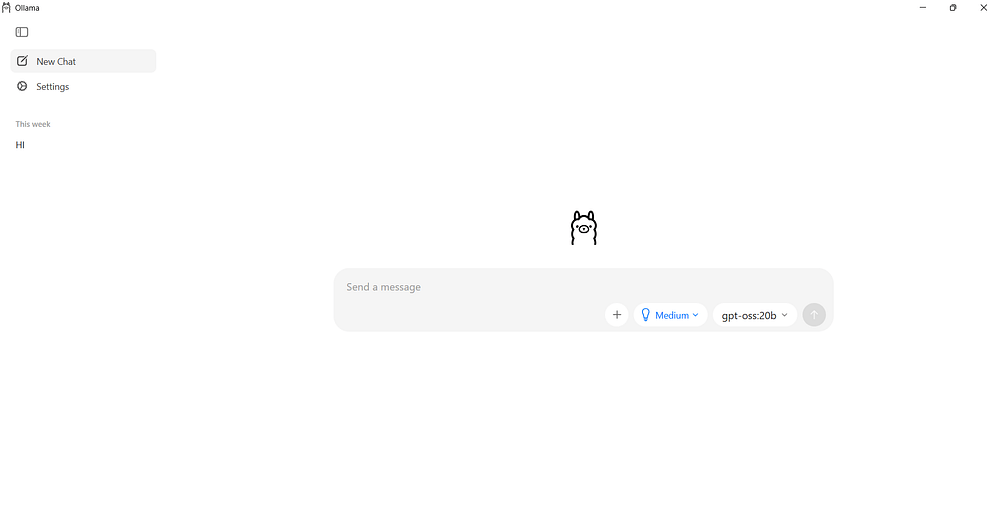
Inside the Ollama interface, you’ll see a simple text box where you can type prompts and receive responses. There’s also a panel that lists available models.

To download and use a model, just select it from the list. Ollama will automatically fetch the model weights and load them into memory.
The first time you ask a question, it will download the model if it does not exist. You can also choose the model from the models search page.
I ll use the gemma 270m model which is the smallest model available in Ollama.

You can see the model being downloaded when used for the first time. Depending on the model size and your system’s performance, this might take a few minutes.
Once loaded, you can start chatting or running tasks directly within the UI. It’s designed to look and feel like a normal chat window, but everything runs locally on your PC.
You don’t need an internet connection after the model has been downloaded.
Installing and Running LLMs via the Command Line
If you prefer more control, you can use the Ollama command-line interface (CLI). This is useful for developers or those who want to integrate local models into scripts and workflows.
To open the command line, search for “Command Prompt” or “PowerShell” in Windows and run it. You can now interact with Ollama using simple commands.
To check if the installation worked, type:
ollama --versionIf you see a version number, Ollama is ready. Next, to run your first model, use the pull command:
ollama pull gemma3:270mThis will download the Gemma model to your machine.

When the process finishes, start it with:
ollama run gemma3:270mOllama will launch the model and open an interactive prompt where you can type messages.

Everything happens locally, and your data never leaves your computer.
You can stop the model anytime by typing /bye.
Managing Models and Resources
Each model you download takes up disk space and memory.
Smaller models like Phi-3 Mini or Gemma 2B are lighter and suitable for most consumer laptops. Larger ones such as Mistral 7B or Llama 3 8B require more powerful GPUs or high-end CPUs.
You can list all installed models using:
ollama list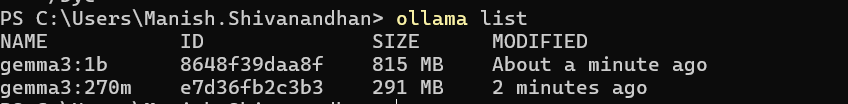
And remove one when you no longer need it:
ollama rm model_nameIf your PC has limited RAM, try running smaller models first. You can experiment with different ones to find the right balance between speed and accuracy.
Using Ollama with Other Applications
Once you’ve installed Ollama, you can use it beyond the chat interface. Developers can connect to it using APIs and local ports.
Ollama runs a local server on http://localhost:11434. This means you can send requests from your own scripts or applications.
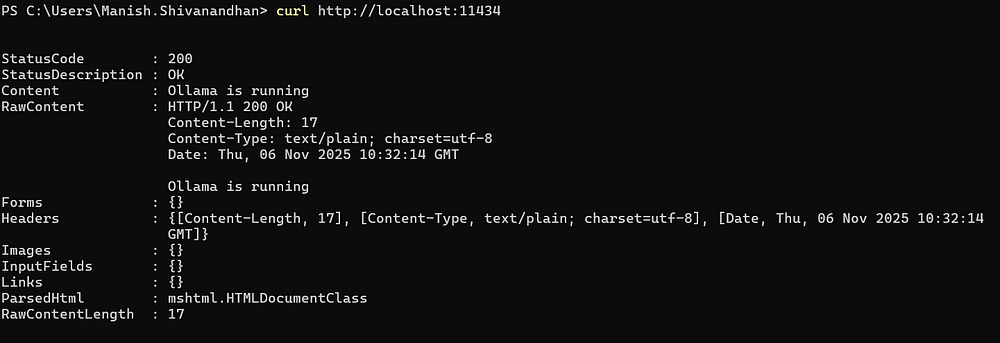
For example, a simple Python script can call the local model like this:
import requests, json
# Define the local Ollama API endpoint
url = "http://localhost:11434/api/generate"
# Send a prompt to the Gemma 3 model
payload = {
"model": "gemma3:270m",
"prompt": "Write a short story about space exploration."
}
# stream=True tells requests to read the response as a live data stream
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, stream=True)
# Ollama sends one JSON object per line as it generates text
for line in response.iter_lines():
if line:
data = json.loads(line.decode("utf-8"))
# Each chunk has a "response" key containing part of the text
if "response" in data:
print(data["response"], end="", flush=True)This setup turns your computer into a local AI engine. You can integrate it with chatbots, coding assistants, or automation tools without using external APIs.Troubleshooting and Common Issues
If you face issues running a model, check your system resources first. Models need enough RAM and disk space to load properly. Closing other apps can help free up memory.
Sometimes, antivirus software may block local network ports. If Ollama fails to start, add it to the list of allowed programs.
If you use the CLI and see errors about GPU drivers, ensure that your graphics drivers are up to date. Ollama supports both CPU and GPU execution, but having updated drivers improves performance.
Why Running LLMs Locally Matters
Running LLMs locally changes how you work with AI.
You’re no longer tied to API costs or rate limits. It’s ideal for developers who want to prototype fast, researchers exploring fine-tuning, or hobbyists who value privacy.
Local models are also great for offline environments. You can experiment with prompt design, generate content, or test AI-assisted apps without an internet connection.
As hardware improves and open source communities grow, local AI will continue to become more powerful and accessible.
Conclusion
Setting up and running an open-source LLM on Windows is now simple. With tools like Ollama and LM Studio, you can download a model, run it locally, and start generating text in minutes.
The UI makes it friendly for beginners, while the command line offers full control for developers. Whether you’re building an app, testing ideas, or exploring AI for personal use, running models locally puts everything in your hands, making it fast, private, and flexible.

